
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Nonlinear compression has become an obligatory technique along with the development of ultrafast lasers in generating ultrashort pulses with narrow pulse widths and high peak power. In particular, techniques of nonlinear compression have experienced a rapid progress as ytterbium (Yb)-doped lasers with pulse widths in the range from hundreds of femtoseconds to a few picoseconds have become mainstream laser tools for both scientific and industrial applications. Here, we report a simple and stable nonlinear pulse compression technique with high efficiency through cascaded filamentation in air followed by dispersion compensation. Pulses at a center wavelength of 1040 nm with millijoule pulse energy and 160 fs pulse width from a high-power Yb:CaAlGdO4 regenerative amplifier are compressed to 32 fs, with only 2.4% loss from the filamentation process. The compressed pulse has a stable output power with a root-mean-square variation of 0.2% over 1 hour.
femtosecond pulse filamentation nonlinear compression High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(6): 06000e84
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610064, China.
2 Key Laboratory of High Energy Density Physics and Technology (MoE), College of Physics, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China.
3 College of Physics, Key Laboratory of High Energy Density Physics and Technology of the Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610064, China.
Mid-infrared (MIR) ultra-short pulses with multiple spectral-band coverage and good freedom in spectral and temporal shaping are desired by broad applications such as steering strong-field ionization, investigating bound-electron dynamics, and minimally invasive tissue ablation. However, the existing methods of light transient generation lack freedom in spectral tuning and require sophisticated apparatus for complicated phase and noise control. Here, with both numerical analysis and experimental demonstration, we report the first attempt, to the best our knowledge, at generating MIR pulses with dual-wavelength spectral shaping and exceptional freedom of tunability in both the lasing wavelength and relative spectral amplitudes, based on a relatively simple and compact apparatus compared to traditional pulse synthesizers. The proof-of-concept demonstration in steering the high-harmonic generation in a polycrystalline ZnSe plate is facilitated by dual-wavelength MIR pulses shaped in both spectral and temporal domains, spanning from 5.6 to 11.4 μm, with multi-microjoule pulse energy and hundred- milliwatt average power. Multisets of harmonics corresponding to different fundamental wavelengths are simultaneously generated in the deep ultraviolet region, and both the relative strength of individual harmonics sets and the spectral shapes of harmonics are harnessed with remarkable freedom and flexibility. This work would open new possibilities in exploring femtosecond control of electron dynamics and light–matter interaction in composite molecular systems.
Ultrafast Science
2023, 3(1): 0022

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China
2 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronics Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 Beijing Center for Crystal Research and Development, Key Laboratory of Functional Crystals and Laser Technology, Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
4 e-mail: liu-jun-1987@live.cn
5 e-mail: jyao@mail.ipc.ac.cn
6 e-mail: hkliang@scu.edu.cn
Nonlinear frequency conversion of wavelength agile and high-power random fiber lasers can provide a promising way to generate continuous-wave (CW) visible and mid-infrared (MIR) light with unique properties such as the continuous modeless spectrum, low temporal/spatial coherence, and high temporal stability. Here, we report a dual-wavelength switchable and tunable random Raman fiber laser (RRFL) based on a phosphosilicate fiber that has two Raman gain peaks for the first time and demonstrate its superior capability to generate widely tunable CW visible and mid-infrared light via nonlinear frequency conversions. By using the combination of a tunable pump and two tunable gratings in Littrow configuration that can provide separated point feedback for the two Stokes wavelengths corresponding to silica- and phosphorus-related Raman peaks, the spectrum of an RRFL can be flexibly manipulated for the aim of nonlinear frequency conversions, including single-wavelength tunable emission at the 1.1 μm or 1.2 μm band for second-harmonic generation (SHG), dual-wavelength simultaneously tunable emission at the 1.1 μm and 1.2 μm bands for the sum-frequency generation (SFG), and dual-wavelength separation tunable emission for difference-frequency generation (DFG). As a result, with the combination of SHG and SFG in a periodically poled lithium niobate crystal array, we experimentally demonstrate the broadest tuning range (560–630 nm) of visible light generated from an RRFL, to the best of our knowledge. The tunable MIR light in the range of 10.7–12.3 μm is also demonstrated through DFG of an RRFL operating in separation tunable dual-wavelength emission mode in a (BGSe) crystal, which is the first realization of CW DFG in the BGSe crystal. We believe the developed dual-wavelength switchable and tunable RRFL can provide a new compact, robust, and cost-effective platform to realize broadly tunable light in both the visible and MIR regions, which can also find potential applications in imaging, sensing, and temporal ghost imaging in various spectral bands.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(5): 808
强激光与粒子束
2021, 33(11): 111004
红外与激光工程
2021, 50(8): 20210396

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China
2 Beijing WaveQuanta Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing 102208, China
3 Hangzhou Yacto Technology Ltd., Hangzhou 311305, China
Lasers with high average and high peak power as well as ultrashort pulse width have been all along demanded by nonlinear optics studies, strong-field experiments, electron dynamics investigations, and ultrafast spectroscopy. While the routinely used titanium-doped sapphire (Ti:sapphire) laser faces a bottleneck in the average power upscaling, ytterbium (Yb)-doped lasers have remarkable advantages in achieving high average power. However, there is still a substantial gap of pulse width and peak power between the Ti:sapphire and Yb-doped lasers. Here we demonstrate a high-power (Yb:CALGO) regenerative amplifier system, delivering 1040 nm pulses with 11 W average power, 50 fs pulse width, and 3.7 GW peak power at a repetition rate of 43 kHz, which to some extent bridges the gap between the Ti:sapphire and Yb lasers. An ultrabroadband Yb-doped fiber oscillator, specially designed spectral shapers, and Yb:CALGO gain medium with broad emission bandwidth, together with a double-end pumping scheme enable an amplified bandwidth of 19 nm and 95 fs output pulse width. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of sub-100 fs regenerative amplifier based on Yb-doped bulk medium without nonlinear spectral broadening. The amplified pulse is further compressed to 50 fs via cascaded-quadratic compression with a simple setup, producing 3.7 GW peak power, which boosts the record of peak power from Yb:CALGO regenerative amplifiers by 1 order. As a proof of concept, pumped by the high-power, 50 fs pulses, 7.5–11.5 µm mid-infrared (MIR) generation via intrapulse difference-frequency generation is performed, without the necessity of nonlinear fiber compressors. It leads to a simple and robust apparatus, and it would find good usefulness in MIR spectroscopic applications.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(8): 08001439
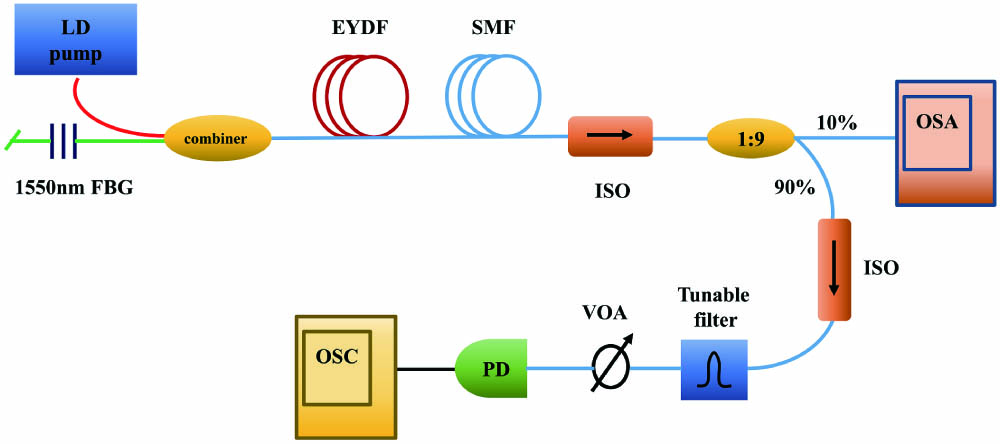
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, China
2 Fiber Optics Research Centre, School of Information and Communication Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
In this Letter, we experimentally investigate fast temporal intensity dynamics and statistical properties of the cladding-pumped Er/Yb co-doped random Rayleigh feedback fiber laser (EYRFL) for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. By using the optical spectral filtering method, strong and fast intensity fluctuations with the generation of extreme events are revealed at the output of EYRFL. The statistics of the intensity fluctuations strongly depends on the wavelength of the filtered radiation, and the intensity probability density function (PDF) with a heavy tail is observed in the far wings of the spectrum. We also find that the PDF of the intensity in the central part of the spectrum deviates from the exponential distribution and has the dependence on the laser operating regimes, which indicates some correlations among different frequency components exist in the EYRFL radiation and may play an important role in the random lasing spectrum stabilization process.
random fiber laser temporal dynamics Rayleigh scattering Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(2): 021402





